2012 was the year the lights came up on the biotech industry. Its claims, its tactics and its products all came under scrutiny and some of its biggest PR fairytales bit the dust. Here are some prime examples.
1. Fleeing Europe: The biotech bubble needs to appear to be constantly expanding but in early 2012 came the news that the GM and chemicals giant BASF was pulling its GM division out of Europe because it was facing opposition “from the majority of consumers, farmers and politicians.” BASF also announced it was stopping the commercialization of its GM Amflora potato, one of only two GM crops authorized for cultivation in the European Union. The crop had been a commercial flop. The industry’s only other crop grown in Europe, Monsanto’s Mon810 GM maize, continued to face bans in a number of countries including France and Germany. Even GM crop trials are in decline and with BASF quitting Europe they’re expected to decline still further.
2. Meltdown in India: Bt cotton in India has been claimed as one of the industry’s biggest success stories but in 2012 the PR claims completely fell apart. First, a leaked agriculture ministry advisory to cotton-growing states admitted, “Cotton farmers are in a deep crisis since shifting to Bt cotton. The spate of farmer suicides in 2011-12 has been particularly severe among Bt cotton farmers.” Two new award winning films also helped expose the truth about GM cotton in India to a wider audience. So too did a powerful report from India’s Parliamentary Committee on Agriculture, after its committee members visited five States, examined thousands of documents and talked to large numbers of farmers and experts. The 31 MPs also met around a hundred widows of Bt cotton farmers, including 14 in a village promoted by Monsanto as a model for Bt cotton’s success. It turned out the farmers inMonsanto’s “model village” wanted a ban on Bt cotton. The shocked MPs issued a unanimous report saying GM crops were not the right way forward for India and called for an immediate ban on all GM crop trials. Not long afterwards an expert panel of scientists set up by lndia’s Supreme Court recommended a 10-year moratorium on GM crops.
3. Opposition grows in the US: Everyone knows about California’s referendum on the labeling of food containing GM ingredients, which was narrowly lost in the face of a massive advertising blitz by its industry opponents. But it took all kinds of lies, dirty tricks and a cool $45 million to kill off the initiative, and still 48.6 percent of voters supported it. Worse still for the industry, the controversy it stirred up helped spread GMO awareness nationwide. Many other states and local governments are now picking up the fight for GMO labeling, while the national Just Label It campaign has already submitted over a million signatures to the FDA asking the agency to require the labeling of GM foods. Some activists even took to the supermarket aisles to label GMO foods themselves. The industry has also been facing street protests across the US, with at least 60 protests targeting Monsanto on the anniversary of the Occupy movement.
4. Opposition grows worldwide: In 2012 protests against GM crop trials and the biotech industry’s activities took place across the globe. And although 60 countries already have GM food labeling, important new breakthroughs were achieved in: India, which is to introduce labeling for the first time in 2013; South Africa, where GM labeling is being tightened up to help enforce food industry compliance; Brazil, where the courts forced the multinational food company Nestle to label GM ingredients in its products; and Turkey, where mandatory labeling is to be extended to include GMO-fed animal products.
5. The reality of GM farming overwhelms public relations – nature cannot be fooled: US farmers are having to use still more pesticides to try and save their crops as infestations of rootworms have exploded on GM (Bt) corn engineered to eradicate them. “I lost $25,000 in yield,” said Charles Sandager, a Minnesota farmer. “They are going to outsmart us, them bugs.” Likewise, in order to combat the ever proliferating numbers of herbicide-resistant superweeds, the GM industry is preparing to roll out crops resistant to older and even more toxic herbicides, as well as to multiple herbicides. Washington State University agronomist Charles Benbrook says what the GM industry is doing “makes about as much sense as pouring gas on a fire to put it out.” Benbrook’s research shows that GM crops, far from cutting agrochemical use in the US as the industry likes to claim, have unleashed a pesticide gusher.
6. Toxics exposed: Among the toxic herbicides GM crops are now being engineered to resist is 2,4-D, a component of Agent Orange. Research has shown 2,4-D to be an endocrine disruptor, and has linked exposure to cancers, neurological impairment and reproductive problems. As a result, Norway, Denmark and Sweden have banned it, but the new wave of 2,4-D-resistant GM crops will massively increase the exposure of farmworkers and consumers to this dangerous herbicide. In 2012 there was also growing evidence of the dangers of Monsanto’s glyphosate-based Roundup herbicide, which with the considerable help of GM Roundup Ready crops is the most heavily used herbicide worldwide:
Glyphosate found in people’s urine – A German university study found significant concentrations of glyphosate in the urine samples of city dwellers. All had concentrations of glyphosate at 5 to 20-fold the limit for drinking water. News of this study came not long after the publication of a study confirming glyphosate was contaminating groundwater. Last year also saw the publication of two US Geological Survey studies which consistently found glyphosate in streams, rain and even air in agricultural areas of the US. Glyphosate has also been found circulating in women’s blood and can even cross the placental barrier and so reach the developing fetus.
Glyphosate and Roundup damage DNA in human mouth cells – A 2012 study by Austrian researchers raises concerns over the safety of inhaling glyphosate, one of the most common ways in which people are exposed to the herbicide in the GM soy-producing countries of South America.
Glyphosate damages nerve cells – A new study adds confirmatory evidence to previous studies that found a correlation between Roundup exposure and Parkinson’s disease.
Roundup can cause amphibians to change shape – A 2012 study found that tadpoles exposed to environmentally relevant concentrations of Roundup grew abnormally large tails.
Roundup kills rat testicular cells – A new study showed that at low doses Roundup reduced testosterone by 35% in mature rats. At high doses, it destroyed testicular cells.
Roundup harms beneficial gut bacteria – A study by scientists at Leipzig University found that Roundup negatively impacted the gastrointestinal bacteria of poultry in vitro. The researchers found that highly pathogenic bacteria resisted Roundup, whereas beneficial bacteria were moderately to highly susceptible to it. The study provides a scientific basis to farmer reports of increased gastrointestinal disease in animals fed GM Roundup Ready soy.
Roundup probably causes birth defects, according to a new peer reviewed paper published in the Journal of Environmental and Analytical Toxicology
7. Monsanto guilty of false advertizing: An advertisement for Roundup that Monsanto placed in Dutch newspapers made a number of misleading claims, according to the Dutch Advertising Code Commission. Earlier in the year, the Advertising Standards Council of India concluded that Monsanto’s claims of economic benefits to farmers from its GM cotton were baseless. Monsanto has also previously been found guilty of using wrong, unproven, misleading and confusing claims to promote either its GM crops or Roundup by advertizing watchdogs in the UK, South Africa and France.
8. Unethical research practices and scientific fraud: In December the Chinese authorities sacked three officials who had approved and conducted a controversial US funded research project that involved testing GM golden rice on school children. The officials were punished for “violating relevant regulations, scientific ethics and academic integrity.” The Chinese investigation into how the research was conducted has also provided evidence that contradicts the claims made about how much golden rice was fed to the children in a paper on the study published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. As a policy researcher at the Chinese Academy of Sciences has commented, “Either the researchers are lying about this now or they lied about it in their paper. It’s a serious offence either way.” Earlier in 2012 came the retraction of a study by researchers at the Monsanto-backed Danforth Center that claimed to have found a way through genetic engineering to boost the protein content of cassava. The retraction occurred “after researchers failed to find any supporting data to back up [the paper’s] claims.” In late 2012 there was also news of researchers studying the Bt toxins used in GM crops having doctored images in a whole series of published papers. Neither of the researchers involved seems to be facing the sack, although one of the researchers is having to step down as head of their university’s Committee on Bioethics! In October of 2012 came the headline, “Top GM researcher falsified patent claim to grab national award.” Back in February 2012 there was yet another remarkable headline, “Untangling India’s Bt cotton fraud: ICAR’s top research institutes and GEAC [the key GM regulator] exposed in Bt cotton research scam.” The scam apparently involved, among other things, stealing a Bt cotton gene from Monsanto, but Monsanto itself and various Indian agricultural universities also stand accused of theft – criminal biopiracy – in the case of another GM crop. And that’s all in just the last 12 months! Some see all this as the result of an over-commercialised public science sector, while others suspect it is the inevitable by-product of GM crops being based on a fraud themselves – a massively hyped technology rooted in entirely false premises.
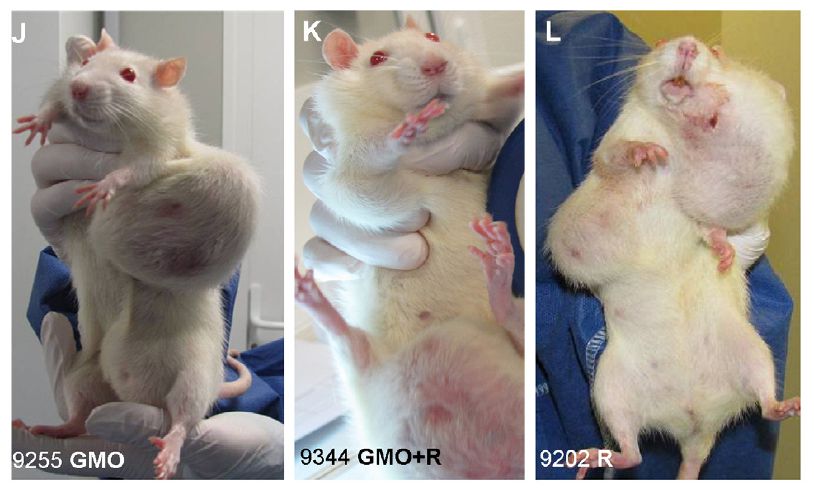
9. Seralini publishes explosive GMO/Roundup study: Prof Gilles-Eric Seralini’s research found serious adverse health impacts in the rats fed Monsanto’s GM corn (NK603) and/or small amounts of the Roundup herbicide that the crop was engineered to withstand. Wave after wave of dubious criticism, fuelled and orchestrated by those with industry connections, attempted to silence the questions raised by the long-term study, as well as to stifle scientific discourse and get the paper retracted. But as the dust starts to settle over the controversy, the study not only remains unretracted but there is a growing recognition of the need for long-term studies on GM crops of the sort Seralini has conducted. Worst of all from the biotech industry’s point of view, their supporters’ savage attacks on Seralini’s study have exposed the fact that a careful comparison of Seralini’s research with Monsanto’s own safety trials shows that if the Seralini experiments are considered insufficient to demonstrate harm, then those carried out by Monsanto cannot prove safety. This is because, whatever its limitations, Seralini’s study was conducted to generally higher scientific standards than the studies underlying GM food approvals. As a result, the attacks on Seralini’s study are bound to fuel calls for mandatory long-term testing of all GMOs and their associated pesticides before they’re commercialized, as well as bringing into question all existing GM crop approvals.
10. Regulatory capture exposed: The other damaging consequence for the biotech industry of the attacks on Seralini and the rush by the likes of the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) to reject the study, has been the resulting exposure of the double standards of regulators who have accepted Monsanto’s studies claiming safety for their products at face value while demanding that public researchers like Seralini prove any harm from GM crops beyond all doubt. This is why 140 French scientists in a public statement published in Le Monde, declared that it was contrary to all scientific ethics to damn an experimental protocol when it gave results that were not wanted, while accepting it when it gave results that were. EFSA’s behaviour has also brought further focus on the problems of regulatory capture and of serious conflicts of interest among the regulators. This was already an open scandal, not least after EU member states earlier in 2012 had had to refuse the nomination of an ex-Monsanto employee to EFSA’s management board. By the end of 2012 there was growing awareness of the extent of regulatory dysfunction and the scandal of government agencies doing exactly what multinational corporations ask them to do.
Source: gmwatch.org


















